Surgery was performed for many years using an “open technique” Small to large incisions ( cuts) were made to allow access to the body and the area involved. The procedures generally were longer and involved extended recovery times.
Laparoscopic or minimally invasive surgery came to the forefront in the 1980’s. Laparoscopy allowed surgeons to use a camera and light to” see” the area for operation. Gynecologists embraced laparoscopic surgery in the 1970’s.The first laparoscopic hysterectomy was performed in 1989.
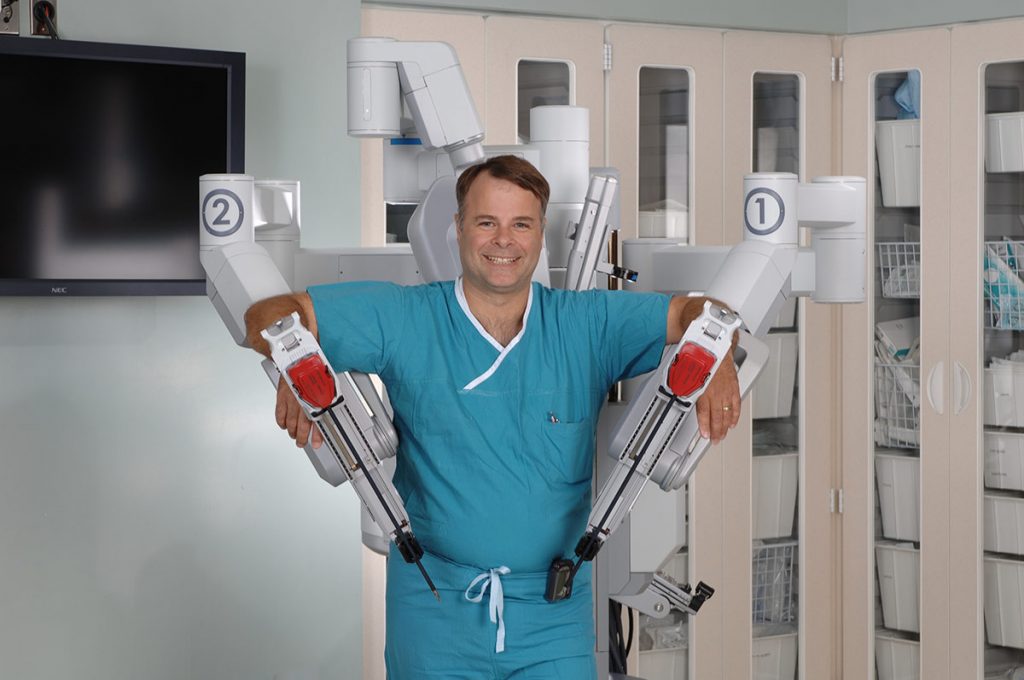
Robotic surgery came on the seen in the late 1990’s and early 2000’s. Robotic surgery is computer assisted and uses a console remote. GYN robotic surgery was FDA approved in 2005. The robot most commonly used today is the Intuitive DaVinci Robot. With the surgeon at the console and the robotic arms attached to the patient, the surgeon uses the remote manipulator to direct the robot arms to perform the actual surgery on the patient. This allows the surgeon better control over the instruments and better view of the surgical site.
The advantages of robotic assisted surgery is less tissue trauma and bleeding, one or a few small incisions, resulting in less blood loss, less pain associated with surgery and reduced recovery times.
In Gynecology, robotic surgery can be performed for:
- Benign Hysterectomy
- Vaginal Vault Prolapse ( Sacrocolpopexy)
- Fibroids
- Endometriosis
- Simple ovarian cystectomy ( cyst removal).
- As technology continues to evolve, so will the use of robotic assisted surgery.